Abstract
Purpose
Autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) is widely used as a part of induction treatment for transplantation-eligible patients with multiple myeloma. For successful ASCT, mobilizing hematopoietic stem cells from bone marrow to peripheral blood is essential because collecting a sufficient number of stem cells using apheresis is mandatory. As a method for mobilization, chemomobilization consisting of high-dose chemotherapy plus granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) or G-CSF alone (G-mobilization) has been used. However, the mobilization failure still remains a problematic issue. Given repeated mobilization attempts increase medical costs and the risk of morbidity related with apheresis, the mobilization process should be efficient. Chemomobilization is more effective than G-mobilization, however, chemomobilization has the risk of complication such as febrile neutropenia or chemotherapy-induced second malignancy. Thus, we compared the efficacy and safety of our new chemomobilization regimen, one-day low-dose etoposide with that of two-day low-dose etoposide, one-day high-dose cyclophosphamide, and G-mobilization.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 234 patients who underwent ASCT for MM between 2008 and 2018 in four tertiary hospitals in Korea. One-day low-dose etoposide regimen (E1) was the intravenous (IV) administration of etoposide (375 mg/m2) over 4 hours whereas two-day low-dose etoposide (E2) was the same dose of etoposide on 1st and 2nd day in outpatient clinic. G-CSF administration was started around on 10th day until the end of collection. In G-mobilization regimen (G), the injection of G-CSF was started four days (day -4) before initiation of apheresis (day 0), and G-CSF once a day was maintained untill the end of collection. One-day high-dose cyclophosphamide regimen (C) was the IV administration of cyclophosphamide (3.5 g/m2) on 1st day and the daily injection of G-CSF from 2nd day until the end of stem cell collection. Peripheral blood stem cell collection was started when CD34-positive cells or hematopoietic progenitor cells were more than 5000/μL in peripheral blood, or white blood cell count was more than 5000/μL. In this study, we defined the 'adequate mobilization' as CD34-positive cells more than 4ⅹ106/kg, and 'mobilization failure' as a collected CD34-positive cells less than 2ⅹ106/kg. Neutrophil and platelet engraftment was defined as more than 500/μL and 20,000/μL on consecutive two days, respectively.
Results
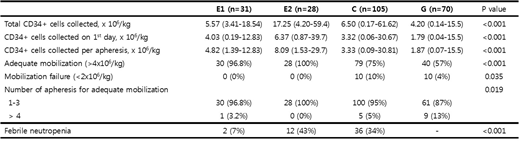
31 patients received single dose etoposide (E1) between 2016 and 2018 whereas 28 patients received double dose etoposide (E2) between 2011 and 2018. The other two regimens were used in 105 (C, 2008-2015) and 70 patients (G, 2008-2017) according to physicians' decision. The comparison of four regimens showed the median CD34-positive cells of E1 regimen was 5.57ⅹ106/kg that was comparable to that of E2 and C (Table 1). The number of CD34-positive cells on 1st day of apheresis was 4.03ⅹ106/kg in E1 regimen, and it was higher than that of C and G (3.32 and 1.79ⅹ106/kg, respectively). As a result, E1 regimen achieved 'adequate mobilization' in 100% of patients (n=30) like E2 regimen (n=28, 100%). Mobilization failure did not occur in E1 and E2 regimens whereas 4-10% of patients experienced mobilization failure in C and G regimens (Table 1). All patients receiving E1 and E2 regimen but one patient in E1 could collect more than 4ⅹ106/kg of CD34-positive cells within three cycles of apheresis. The occurrence of febrile neutropenia was extremely lower in E1 regimen (7%) than E2 and C regimens (43% and 34%, respectively, p<0.001). Both neutrophil and platelet engraftment were the fastest in E1 (the median 9 days after ASCT, p<0.001).
Conclusions
One-day low-dose etoposide administration could be effective for chemomobilization in myeloma patients with reduced risk of complication compared to two-day low-dose etoposide, high-dose cyclophosphamide and G-mobilization.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal